Andrea Ghez Wins Nobel Prize In Physics

The First Distance Measurement to a Magnetar in Our Galaxy
September 29, 2020
Anemic Star Cluster Breaks Metal-Poor Record
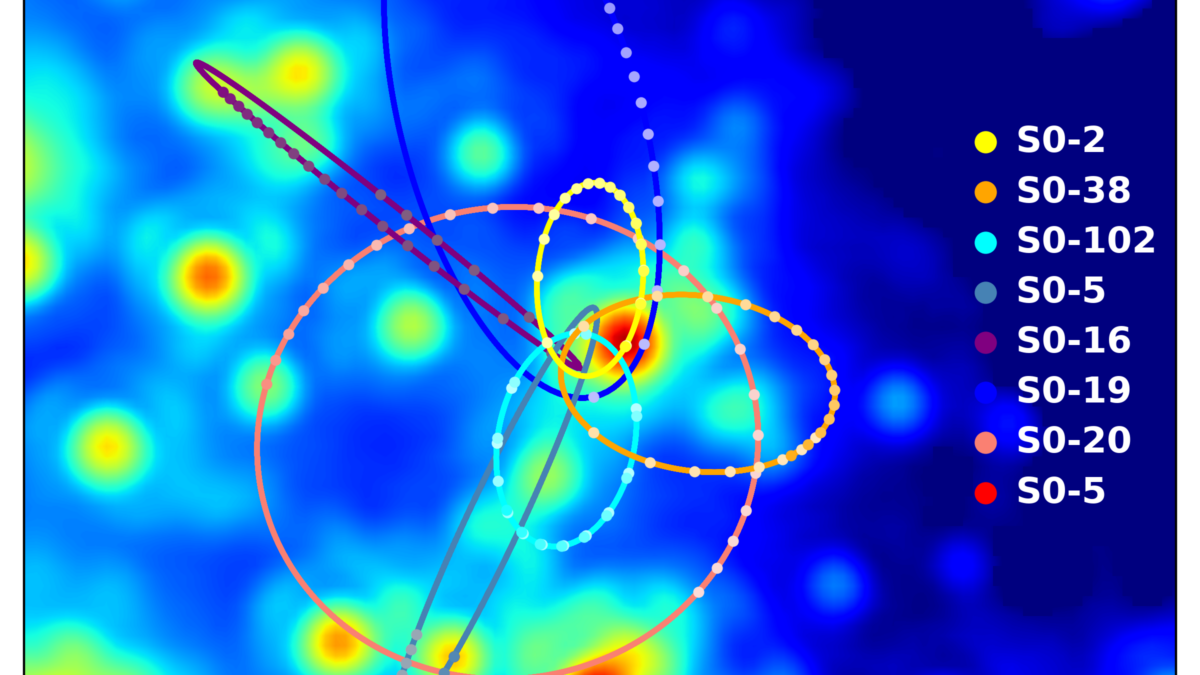
October 21, 2020Dr. Andrea Ghez, an astrophysicist at UCLA who has been observing the Galactic Center from Maunakea for over two decades, has won the 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics. She is honored for her pioneering work using W. M. Keck Observatory to provide conclusive experimental evidence of a supermassive black hole with the mass of four million suns residing at the center of our Milky Way galaxy.
Read more in the W M Keck Observatory Press Release.